What Are Bullet Proof Vests Made Of?
In the realm of personal protection, few items carry the mystique and life-saving potential of bullet proof vests. These vests, also known as ballistic vests or body armor, are crucial for individuals working in law enforcement, military, security, and even civilians facing potential threats. But what exactly are bulletproof vests made of, and how do they work?
Understanding the Basics
Bullet proof vests are designed to protect the wearer from projectiles, including bullets and shrapnel, by absorbing and dispersing the energy of the impact. They come in various levels of protection, categorized by the types of firearms they can withstand and the velocity of the bullets. While no vest can offer 100% protection against all threats, they significantly increase the wearer’s chances of survival in dangerous situations.
Layers of Protection
At the heart of a bulletproof vest lies layers of specialized materials engineered to withstand high-velocity impacts. The primary components of these layers include:
1. Ballistic Fabric
The most common material used in bulletproof vests is Kevlar, a synthetic fiber developed by DuPont in the 1960s. Kevlar is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio and is used in a wide range of protective applications, from body armor to ropes and tires. Kevlar fibers are incredibly strong and resistant to penetration, making them ideal for stopping bullets.
2. Aramid Fibers
Apart from Kevlar, other aramid fibers such as Twaron and Spectra are also used in bulletproof vests. These fibers offer similar properties to Kevlar, providing high tensile strength and energy absorption capabilities.
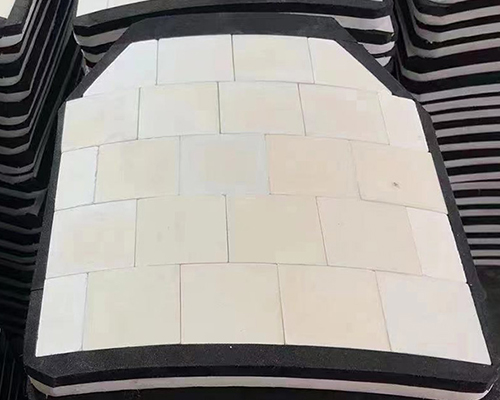
3. Ceramic Plates
In addition to ballistic fabric, some vests incorporate ceramic plates, typically made from materials like boron carbide or silicon carbide. These plates provide additional protection against high-velocity rifle rounds by shattering the bullet upon impact, dispersing its energy and preventing penetration.

4. Metal or Polymer Components
Some vests include metal or polymer components for structural support and to distribute the force of impact more evenly across the wearer’s body.
How They Work
When a bullet strikes a bulletproof vest, the layers of ballistic fabric and other materials work together to dissipate the energy of the projectile. The fibers in the fabric stretch and deform, absorbing the kinetic energy of the bullet and spreading it over a larger area. Meanwhile, ceramic plates fracture upon impact, further slowing down the bullet and preventing it from penetrating the vest.
Conclusion
Bullet proof vests represent a remarkable fusion of advanced materials science and protective design. By harnessing the strength and resilience of materials like Kevlar and ceramic, these vests provide an essential layer of defense for those facing potential ballistic threats in their line of duty or everyday life.
While the materials used in bulletproof vests continue to evolve and improve, their fundamental purpose remains unchanged: to safeguard lives and give wearers a fighting chance in the face of danger. As technology advances, we can expect further enhancements in both the protective capabilities and comfort of these lifesaving garments, ensuring that those who wear them are better equipped to confront the challenges of an uncertain world.
